Smart Seller Manager
Objective
Manual
The attached file contains a summary of the Smart Seller Management feature and the best way to setup rules.
Terminology
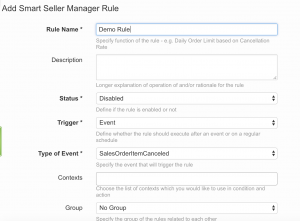
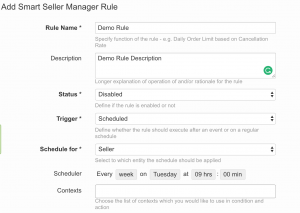
Status
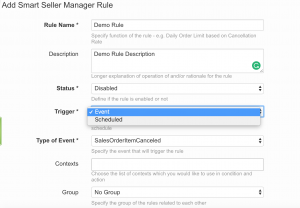
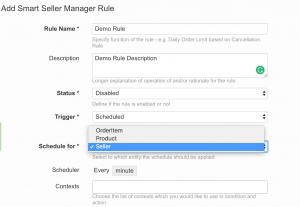
Trigger
Scheduled for
Scheduler
- Every week on every day of the week at 18 hours and 30 minutes
- Every week on every day of the week at 18 hours and 30 minutes
- Every month on the 1st at 18 hours and 20 hours and 00 minutes
- Every hour at 5 minutes past the hour
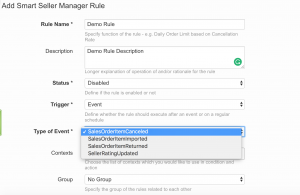
If “Event” is selected as type the event needs to be further specified in the following:
Event
- SalesOrderItemReturned
- SalesOrderItemImported
- SalesOrderItemCanc
- SellerRatingUpdated
The first part of the event name describes the context of the event for example: Sales Order Item, Seller or Product. The second part describes the actual event for example: When Sales Order Item is Returned the rule is executed and the conditions are checked.
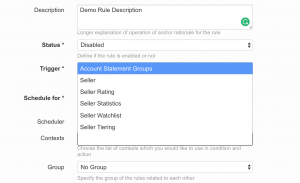
Contexts
- Account Statements Groups
- Order
- Order Item
- Order Item Precalculated Transactions
- Order Item Transactions
- Product
- Product Quality Control
- Product Statistics
- Seller
- Seller Rating
- Seller Statistics
- Seller Watchlist (deprecated)
- Seller Tags
- Seller Tiering
Condition
Classification of available conditions
- F – Functions – if it is a function then you need to add “()”. For example, Timing.now(), Timing.now().format(“Y-m-d”)
- I – Integer
- B – Boolean
- S – String
- O – Object
- D – Decimal
| Group | Attribute | Description | Classification | Example |
| Timing | Timing.weekdaySunday | The numerical representation of Sunday (0) | I | Timing.weekdaySunday == false |
| Timing.weekdayMonday | The numerical representation of Monday (1) | I | Timing.weekdayMonday == true | |
| Timing.weekdayTuesday | The numerical representation of Tuesday (2) | I | Timing.weekdayTuesday or Timing.weekdayMonday == true | |
| Timing.weekdayWednesday | The numerical representation of Wednesday (3) | I | orderItem.status == orderItemStatuses.pending and Timing.weekdayWednesday | |
| Timing.weekdayThursday | The numerical representation of Thursday (4) | I | ||
| Timing.weekdayFriday | The numerical representation of Friday (5) | I | ||
| Timing.weekdaySaturday | The numerical representation of Saturday (6) | I | ||
| Timing.now | Returns the current time in seconds | F | Timing.now().diff(orderItem.readyToShipAt) > 2880 | |
| Timing.startedAt | Returns the time when the script started | F | Timing.startedAt().diff(orderItem.readyToShipAt) > 2880 | |
| Timing.parse | Converts the given textual object to a time object. To see what can be used please refer to this link | F |
Timing.parse(“7 days ago”)
| |
| Timing.isWeekend | Is the given time a weekend for the Seller or in general if Seller Id was not provided | F | Timing.isWeekend =! true | |
| Timing.isHoliday | Is the given time a holiday for the Seller or in general if Seller Id was not provided | F | Timing.now().isHoliday | |
| Timing.beginningOfThisDay | Returns the beginning of this day time | F | ||
| Timing.beginningOfThisWeek | Returns the beginning of this week time | F | ||
| Timing.beginningOfThisMonth | Returns the beginning of this month time | F | ||
| Timing.beginningOfThisYear | Returns the beginning of this year time | F | ||
| Available for all Timing functions mentioned above | Timing. … .format | Formats the Timing Object according to a defined format, by default that is Y-m-d\TH:i:s for available formats please check here | F | Timing.now().format(“Y-m-d”) |
| Timing. … .year | Full numeric representation of a year in 4 digits | F | ||
| Timing. … .month | Returns the numeric representation of a month from 1 to 12 | F | ||
| Timing. … .day | Returns the numeric representation of the day of a month from 1 to 31 | F | ||
| Timing. … .week | Returns the number of the week of a year | F | ||
| Timing. … .weekday | Returns the numeric representation of the day of the week from 0 (Sunday) to 6 (Saturday) | F | ||
| Timing. … .hour | Returns the numeric representation of the hour of the day from 0 to 23 | F | ||
| Timing. … .diff | The difference between the current timing object and provided parameter in seconds. If the parameter is earlier than the object, the result is positive | F | Timing.now().diff(orderItem.readyToShipAt) > 129600 | |
| Timing. … .addDays | Adds an amount of days | F | ||
| Timing. … .addWeeks | Adds an amount of weeks | F | ||
| Timing. … .addMonths | Adds an amount of months | F | ||
| Timing. … .addYears | Adds an amount of years | F | ||
| Timing. … .subDays | Subtracts an amount of days | F | ||
| Timing. … .subWeeks | Subtracts an amount of weeks | F | ||
| Timing. … .subMonths | Subtracts an amount of months | F | ||
| Timing. … .subYears | Subtracts an amount of months | F | ||
| Math | Math.ceil | Rounds up fractions | F | |
| Math.round | Returns the rounded value of a value to specific precision | F | ||
| Math.floor | Rounds fractions down | F | ||
| Math.abs | Absolute value | F | ||
| Math.max | Find highest value | F | Math.max(10) | |
| Math.min | Find lowest value | F | Math.min(1) | |
| Category | Category.isInSubtree | Checks if a category is in a subtree | F | Category.isInSubtree (12) |
| PendingTransactions | PendingTransactions.countPendingTransactionsBySeller | Returns the amount of pending transactions of the Seller with the given account statement group. The parameters are: SellerId (I required), accountStatementGroupId (I optional), startDate (TimingObject optional), endDate (TimingObject optional) | F | PendingTransactions.countPendingTransactionsBySeller(seller.id,accountStatementGroups.get(“Customer Compensation for Bad Quality Items”).id,Timing.parse(“7 days ago”),Timing.now()) > 0 |
| Transactions | Transactions.countTransactionsBySeller | Returns the amount of transactions of the Seller with the given account statement group. The parameters are: SellerId (I required), accountStatementGroupId (I optional), startDate (TimingObject optional), endDate (TimingObject optional) | F | Transactions.countTransactionsBySeller(seller.id,accountStatementGroups.get(“Customer Compensation for Bad Quality Items”).id,Timing.parse(“7 days ago”),Timing.now()) > 0 |
| Order item Shipment Types | orderItemShipmentTypes.cossDocking | Returns cross-docking shipment type for an order item | I | orderItem.shipmentType == orderItemShipmentTypes.cossDocking |
| orderItemShipmentTypes.dropShipping | Returns dropshipping shipment type for an order item | I | ||
| orderItemShipmentTypes.ownWarehouse | Returns own warehouse shipment type for an order item | I | ||
| Order Item Statuses | orderItemStatuses.pending | Returns pending status of item | S | |
| orderItemStatuses.shipped | Returns shipped status of item | S | ||
| orderItemStatuses.canceled | Returns cancelled status of item | S | ||
| orderItemStatuses.failed | Returns failed status of item | S | ||
| orderItemStatuses.delivered | Returns delivered status of items | S | ||
| orderItemStatuses.readyToShip | Returns ready to ship status of item | S |
| Context | Attribute | Classification | Description | Example |
| Seller | seller.id | Internal Seller Center ID of Seller | I | Timing.isWeekend(Timing.now(),seller.id) == false |
| seller.shortCode | Seller identifier aka Seller Shortcode or Seller Id | S | ||
| seller.age | Seller age on the platform since registration in days | I | seller.age > 30 | |
| seller.hasTag | Checks whether the given seller has tags assigned | B | Timing.isWeekend(Timing.now(),seller.id) == false and seller.hasTag() == true | |
| seller.hasAssignedTags | The name of the tag assigned to a Seller | F | seller.hasAssignedTags([“Tag1″,”Tag2”]) == true | |
| seller.email | Seller email | S | ||
| seller.taxClass | Seller tax class which is either local or international | S | seller.taxClass = international | |
| seller.currentTier | The representation of the current Seller tier | S | ||
| Seller Rating | sellerRating.rating | Seller ranking, a value between 0.00 and 5.00 | D | sellerRating.rating =! 0 |
| sellerRating.hasRating | Whether the Seller has a rating | B | sellerRating.rating =! 0 and sellerRating.hasRating | |
| sellerRating.cancellationRate | Check the Seller’s cancellation rate, a value between 0.00 and 1.00 representing a percentage | D | sellerRating.cancellationRate = 0.1 | |
| sellerRating.hasCancellationRate | Whether the Seller has a cancellation rate | B | ||
|
sellerRating.returnRate (not implemented) |
Check the Seller’s return rate, a value between 0.00 and 1.00 representing a percentage (not implemented) |
D | ||
|
sellerRating.hasReturnRate (not implemented) |
Whether the Seller has a return rate (not implemented) |
B | ||
| sellerRating.readyToShip24hRate | Check the Seller’s ready to ship 24hr rate, a value between 0.00 and 1.00 representing a percentage | D | ||
| sellerRating.hasReadyToShip24hRate | Whether the Seller has a ready to ship 24hr rate | B | ||
| sellerRating.shipped24hRate | Check the Seller’s pending to shipped in 24hr rate, a value between 0.00 and 1.00 representing a percentage | D | ||
| sellerRating.hasShipped24hRate | Whether the Seller has a pending to shipped in 24hr rate | B | ||
| sellerRating.shipped48hRate | Check the Seller’s pending to shipped in 48hr rate, a value between 0.00 and 1.00 representing a percentage | D | ||
| sellerRating.hasShipped48hRate | Whether the Seller has a pending to shipped in 48hr rate | B | ||
| sellerRating.shipOnTimeRate | Check the Seller’s ship on time rate, a value between 0.00 and 1.00 representing a percentage | D | ||
| sellerRating.hasShipOnTimeRate | Whether the Seller has a ship on time rate | B | ||
| sellerRating.averageRating | Checks the Seller’s average rating over the past 3 months | D | ||
| sellerRating.hasAverageRating | Whether the Seller has an average rating | B | ||
| Seller Statistics | sellerStatistics.itemsSold | Number of gross items sold over the last D days | D | |
| sellerStatistics.averageItemsFulfilled | Average value of (Items sold – items cancelled) daily, calculated over a number of days with min. one order, over the last 2 weeks | D | ||
| sellerStatistics.itemsForPeriod | Amount of (items sold – items cancelled) over the last M calendar months | I | ||
| Seller Tags | sellerTags.productsAmount |
Amount of products which are tagged for the current seller
|
I | sellerTags.productsAmount > 1 |
| sellerTags.hasProducts | Whether the seller has products which are tagged or not | B | sellerTags.hasProducts == true | |
| sellerTags.orderItemsAmount | Amount of order items which are tagged for the current Seller | I | sellerTags.orderItemsAmount < 10 | |
| sellerTags.hasOrderItems | Whether the Seller has order items on which are tagged or not | B | sellerTags.hasOrderItems < 10 | |
| Seller Tiering | tiering.has | Checks if tier with given name exists | F | |
| tiering.get | Returns a tier by a given name | F | (seller.age == 0 or seller.age >= tiering.get(“argent”).getAttr(“sellerAge”)) | |
| tiering.get.name | Tier context name (system name) | S | ||
| tiering.get.displayName | Tier display name (human readable) | S | ||
| tiering.get.hasAttr | Check if an Attribute for a tier with given name exists | F | ||
| tiering.get.getAttr | Returns an attribute of a tier by given name | F | (seller.age == 0 or seller.age >= tiering.get(“argent”).getAttr(“sellerAge”)) | |
| Account Statement Groups | accountStatementGroups.has | Checks if an account statement group with a given name exists, required parameter is a string with the name | F | accountStatementGroups.has (“Commission”) |
| accountStatementGroups.get | Returns an account statement group with a given name, required parameter is a string with the name | F | accountStatementGroups.get (“Commission”) | |
| accountStatementGroups.id | Returns an account statement group with a given account statement group Id | I | ||
| accountStatementGroups.name | Returns an account statement group with a given human readable account statement group name | S | ||
| accountStatementGroups.transactionTypeId | Returns an account statement group with a associated transaction type Id | U |
| Context | Attribute | Classification | Description | Example |
| Seller | seller.id | Internal Seller Center ID of Seller | I | Timing.isWeekend(Timing.now(),seller.id) == false |
| seller.shortCode | Seller identifier aka Seller Shortcode or Seller Id | S | seller.shortCode == “TH435” | |
| seller.age | Seller age on the platform since registration in days | I | seller.age > 10 | |
| seller.hasTags | Checks whether the given Seller has tags assigned | B | seller.hasTags == true | |
| seller.hasAssignedTags | The name of the tag(s) assigned to a sellers | F | seller.hasAssignedTags([“Tag1″,”Tag2”]) | |
| seller.email | Seller email | S | ||
| seller.taxClass | Seller tax class which is either local or international | S | seller.taxClass == “international” | |
| seller.currentTier | The representation of the current Seller tier | S | ||
| Seller Rating | sellerRating.rating | Seller ranking, a value between 0.00 and 5.00 | D | sellerRating.rating > 2 |
| sellerRating.hasRating | Whether the Seller has a rating | B | ||
| sellerRating.cancellationRate | Check the Seller’s cancellation rate, a value between 0.00 and 1.00 representing a percentage | D | ||
| sellerRating.hasCancellationRate | Whether the Seller has a cancellation rate | B | ||
| sellerRating.returnRate | Check the Seller’s return rate, a value between 0.00 and 1.00 representing a percentage | D | ||
| sellerRating.hasReturnRate | Whether the Seller has a return rate | B | ||
| sellerRating.readyToShip24hRate | Check the Seller’s ready to ship 24hr rate, a value between 0.00 and 1.00 representing a percentage | D | ||
| sellerRating.hasReadyToShip24hRate | Whether the Seller has a ready to ship 24hr rate | B | ||
| sellerRating.shipped24hRate | Check the Seller’s pending to shipped in 24hr rate, a value between 0.00 and 1.00 representing a percentage | D | ||
| sellerRating.hasShipped24hRate | Whether the Seller has a pending to shipped in 24hr rate | B | ||
| sellerRating.shipped48hRate | Check the Seller’s pending to shipped in 48hr rate, a value between 0.00 and 1.00 representing a percentage | D | ||
| sellerRating.hasShipped48hRate | Whether the Seller has a pending to shipped in 48hr rate | B | ||
| sellerRating.shipOnTimeRate | Check the Seller’s ship on time rate, a value between 0.00 and 1.00 representing a percentage | D | ||
| sellerRating.hasShipOnTimeRate | Whether the Seller has a ship on time rate | B | ||
| sellerRating.averageRating | Checks the Seller’s average rating over the past 3 months | D | ||
| sellerRating.hasAverageRating | Whether the Seller has an average rating | B | ||
| Seller Statistics | sellerStatistics.itemsSold | Number of gross items sold over the last D days | D | |
| sellerStatistics.averageItemsFulfilled | Average value of (Items sold – items cancelled) daily, calculated over a number of days with min. one order, over the last 2 weeks | D | ||
| sellerStatistics.itemsForPeriod | Amount of (items sold – items cancelled) over the last M calendar months | I | ||
| Seller Tags | sellerTags.productsAmount | Amount of products which are tagged for the current Seller | I | |
| sellerTags.hasProducts | Whether the Seller has tagged products or not | B | ||
| sellerTags.orderItemsAmount | Amount of order items which are tagged for the current Seller | I | ||
| sellerTags.hasOrderItems | Whether the seller has tagged order items or not | B | ||
| Seller Tiering | tiering.has | Checks if tier with given name exists | F | |
| tiering.get | Returns a tier by a given name | F | ||
| tiering.get.name | Tier context name (system name) | S | ||
| tiering.get.displayName | Tier display name (human readable) | S | ||
| tiering.get.hasAttr | Check if an Attribute for a tier with given name exists | F | ||
| tiering.get.getAttr | Returns an attribute of a tier by given name | F | ||
| Account Statement Groups | accountStatementGroups.has | Checks if an account statement group with a given name exists, required parameter is a string with the name | F | |
| accountStatementGroups.get | Returns an account statement group with a given name, required parameter is a string with the name | F | accountStatementGroups.get(“Customer Compensation for Bad Quality Items”) | |
| accountStatementGroups.id | Returns an account statement group with a given account statement group Id | I | ||
| accountStatementGroups.name | Returns an account statement group with a given human readable account statement group name | S | ||
| accountStatementGroups.transactionTypeId | Returns an account statement group with a associated transaction type Id | U | ||
| Order | order.id | Seller Center internal order id | I | |
| Order Item Precalculated Transactions | orderItemPrecalculatedTransactions.hasByGroup | Whether an order item has a precalulated transaction in the given account statement group. The account statement group needs to be defined as string. | F | |
| orderItemPrecalculatedTransactions.getSumByGroup | Returns the sum of all order item with precalulated transaction in the given account statement group. The account statement group needs to be defined as string. | F | ||
| Order Item Transactions | orderItemPrecalculatedTransactions.hasByGroup | Whether an order item has a precalulated transaction in the given account statement group. The account statement group needs to be defined as string. | F | |
| orderItemPrecalculatedTransactions.getSumByGroup | Returns the sum of all order item with precalulated transaction in the given account statement group. The account statement group needs to be defined as string. | F | ||
| Product | product.id | Internal Seller Center Id of the product | I | |
| product.sku | Product SKU | S | ||
| product.productSetId | Product set Id | I | ||
| product.primaryCategoryId | Product primary category Id | I | ||
| product.hasTag | Whether a product is tagged | B | ||
| product.hasAssignedTags | Checks if tag mentioned in the function are assigned to the given product | F | product.hasAssignedTags([“tag 1″,”tag 2”]) | |
| product.qcStatus | The product quality control status of a product | S | ||
| product.rejectReason | The reason a product was rejected from quality control | S | ||
| Product Statistics | productsStatistic.returnRate | Provides option to check the return rate of a product | D | |
| productsStatistic.rejectionRate | Provides option to check the rejection rate of a product | D | ||
| productsStatistic.dailySales | Amount of order items which were created on that day | I | ||
| Product Quality Control | productQc.rejectReason | Project quality reject reason list | A | (“reason 1” in productQc.rejectReasons) or (“reason 2” in productQc.rejectReasons) |
| Context | Attribute | Classification | Description | Example |
| Seller Tiering | tiering.has | Checks if tier with given name exists | F | |
| tiering.get | Returns a tier by a given name | F | ||
| tiering.get.name | Tier context name (system name) | S | ||
| tiering.get.displayName | Tier display name (human readable) | S | ||
| tiering.get.hasAttr | Check if an Attribute for a tier with given name exists | F | ||
| tiering.get.getAttr | Returns an attribute of a tier by given name | F | ||
| Account Statement Groups | accountStatementGroups.has | Checks if an account statement group with a given name exists, required parameter is a string with the name | F | |
| accountStatementGroups.get | Returns an account statement group with a given name, required parameter is a string with the name | F | accountStatementGroups.get(“Customer Compensation for Bad Quality Items”) | |
| accountStatementGroups.id | Returns an account statement group with a given account statement group Id | I | ||
| accountStatementGroups.name | Returns an account statement group with a given human readable account statement group name | S | ||
| accountStatementGroups.transactionTypeId | Returns an account statement group with a associated transaction type Id | U | ||
| Product | product.id | Internal Seller Center Id of the product | I | |
| product.sku | Product SKU | S | ||
| product.productSetId | Product set Id | I | ||
| product.primaryCategoryId | Product primary category Id | I | ||
| product.hasTags |
Whether a product has tags assigned
Critical KnowledgeWatchlist will be replaced by tags managed by the Tag Manager feature by the end of Q3 2017
|
B | ||
| product.hasAssignedTags | Checks if tag mentioned in the function are assigned to the given product | F | product.hasAssignedTag([“tag1″,”tag2”]) | |
| product.qcStatus | The product quality control status of a product | S | ||
| product.rejectReason | The reason a product was rejected from quality control | S | ||
| Product Statistics | productsStatistic.globalReturnRate | Provides option to check the global return rate of a product | D | |
| productsStatistic.rejectionRate | Provides option to check the rejection rate of a product | D | ||
| productsStatistic.dailySales | Amount of order items which were created on that day | I | ||
| productStatistic.numberOfGlobalReturns | Returns the number of times a product has been returned calculated over the same time as the globalReturnRate | |||
| Product Quality Control | productQc.rejectReason | Project quality reject reason list | A | (“reason 1” in productQc.rejectReasons) or (“reason 2” in productQc.rejectReasons) |
Operators
-
+ (addition)
- Example: In transaction generation you may put as net value “orderItemTransactions.getSumByGroup(accountStatementGroups(“Commission”)) + 100″ add 100 to sum of all commissions for an order item
-
– (subtraction)
- Example: In transaction generation you may put as net value “orderItemTransactions.getSumByGroup(accountStatementGroups(“Commission”)) – 100″ subtract 100 from sum of all commissions for an order item
-
* (multiplication)
- Example: In transaction generation you may put as net value “orderItemTransactions.getSumByGroup(accountStatementGroups(“Commission”)) * -1″ change sign (to negative) for sum of order item commissions
-
/ (division)
- Example: In transaction generation you may put as net value “orderItemTransactions.getSumByGroup(accountStatementGroups(“Commission”)) / 10″ divide sum of order item commissions by 10
-
% (modulus)
- Example: (Timing.now().year % 4 ) == 0 // Leap year
-
** (pow)
- Example: In transaction generation you may put as net value “orderItemTransactions.getSumByGroup(accountStatementGroups(“Commission”)) ** 2″ raise to power of 2 sum of order item commissions
-
== (equal)
- Example: sellerRating.hasGlobalCancellationRate == true
-
=== (identical)
- Checks that both comparing side has same value and same type (boolean/string/integer, etc..), seller.taxClass === ‘local’
-
!= (not equal)
- Example: orderItem.shipmentType != OrderItemShipmentTypes.dropShipping
-
!== (not identical)
- In addition of checking values, the operator also compares for types (boolean/string/integer, etc..), orderItem.returnReason !== “Quality – item counterfeit”
-
< (less than)
- Example: seller.age < 30
-
> (greater than)
- Example: Timing.now().diff(orderItem.createdAt) > 25200 – if order item was created more than 7 hours ago
-
<= (less than or equal to)
- Example: seller.age <= 30
-
>= (greater than or equal to)
- Example: seller.age >= 30
-
matches (regex match)
- Example: “1020202” matches “/([0-9]+)/g”
-
not or !
- Example: !Timing.isHoliday(Timing.now(),seller.id)
-
and or &&
- Example: seller.taxClass == ‘global’ and orderItem.status == OrderItemStatuses.readyToShip
-
or or ||
- Example: seller.taxClass == ‘global’ and orderItem.status || OrderItemStatuses.readyToShip
-
~ (concatenation)
- Example: “Seller has ” ~ sellerTags.productsAmount ~ ” of products tagged”
-
in (contain)
- Example: seller.shortCode in [‘NG101Y9′,’NG10A0F’]
-
not in (does not contain)
- Example: seller.shortCode not in [‘NG101Y9′,’NG10A0F’]
-
.. (range)
- Example: seller.age in 18..45
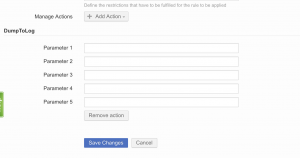
Actions
To assign a tag to an entity just select tag name from the dropdown for the action, the expiry time of the tag will be displayed in the list. The expiry countdown begins as soon as the tag was assigned to the entity.
To link to tagged products simply use: [sellercenter url]/product/index/tagged
To link to tagged order items use: {development on going}
|
|
Disclaimer:
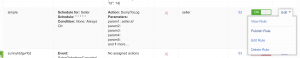
Rule Setup
Deferred Actions
Sample Rule Setup
| Rule Group | Rule Name | Description | Type | Contexts | Defer | Condition | Action |
| Late Fulfilment Education | Add Tag to Pending Items | Assign a tag (“Late Fulfilment”) to order items every day at 6am which are pending and will be go over the defined SLA time in the next 48 hours |
|
orderItem, orderItemStatuses, orderItemShipmentTypes, seller | No | orderItem.shipmentType == orderItemShipmentTypes.dropShipping and Timing.isWeekend(Timing.now(),seller.id) == false and Timing.isHoliday(Timing.now(),seller.id) == false and orderItem.status == orderItemStatuses.pending and Timing.now().diff(orderItem.createdAt) >172800 and Timing.now().weekday() != Timing.weekdayMonday |
AddToWatchlist
|
| Late Fulfilment Education | Send warning popup for order items on Watchlist | Tags Sellers as target of warning popup sent on regular basis. |
|
seller, sellerWatchlist | No | sellerWatchlist.hasOrderItems == true |
AddSellerTag
|
| Late Fulfilment Education | Send preventive e-mail for order items on Watchlist | Sends warning email every day at 7am to Sellers who have order items on watchlist at a defined point in time |
|
seller, sellerWatchlist | No | sellerWatchlist.hasOrderItems == true |
Send Email
|
| Late Fulfilment Education | Cancel pending order items | Cancels all order items which are on Watchlist and still pending (have not been processed) at 10pm |
|
seller, sellerWatchlist | No | sellerWatchlist.hasOrderItems == true and orderItem.status == OrderItemStatuses.pending |
Set Order Item to Canceled
|
Troubleshooting hints
There may be a need to understand why certain rules were not triggered nor executed. Fortunately, Smart Seller Manager comes with extensive logging, through Kibana. We recommend to use the following queries as an investigation / troubleshooting pattern: